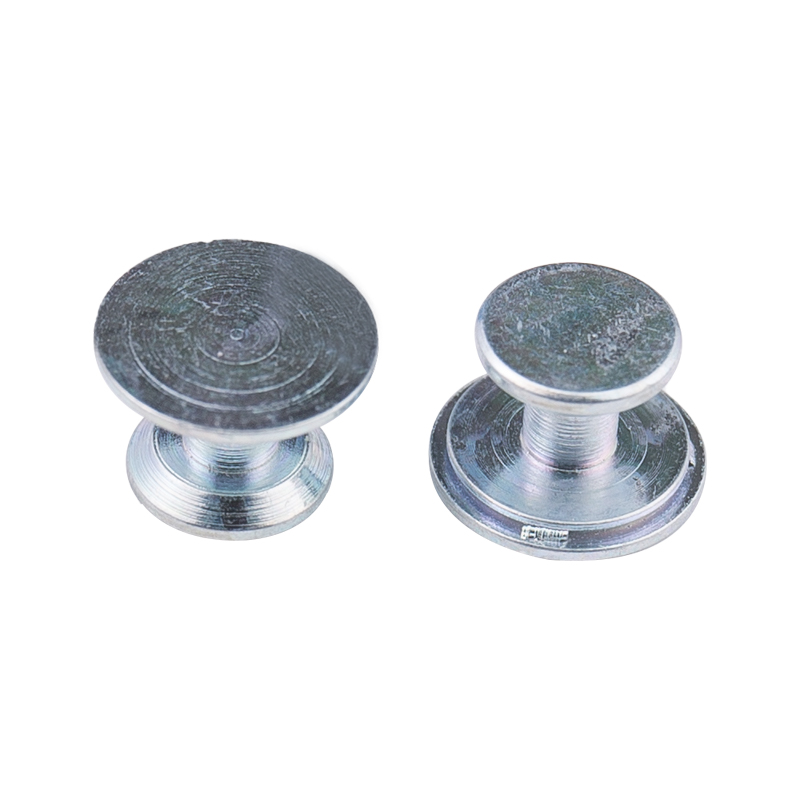
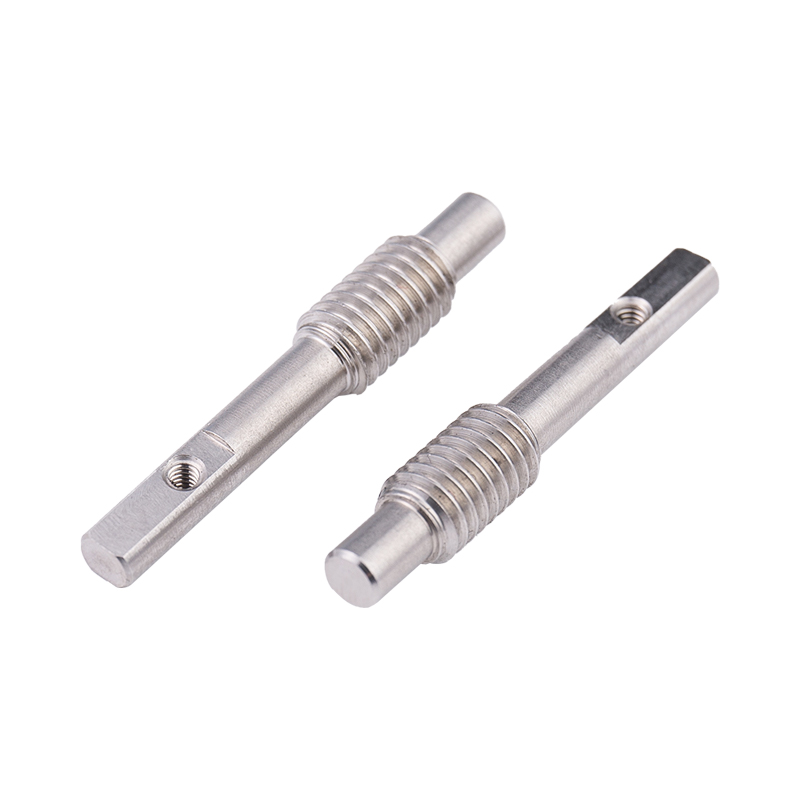
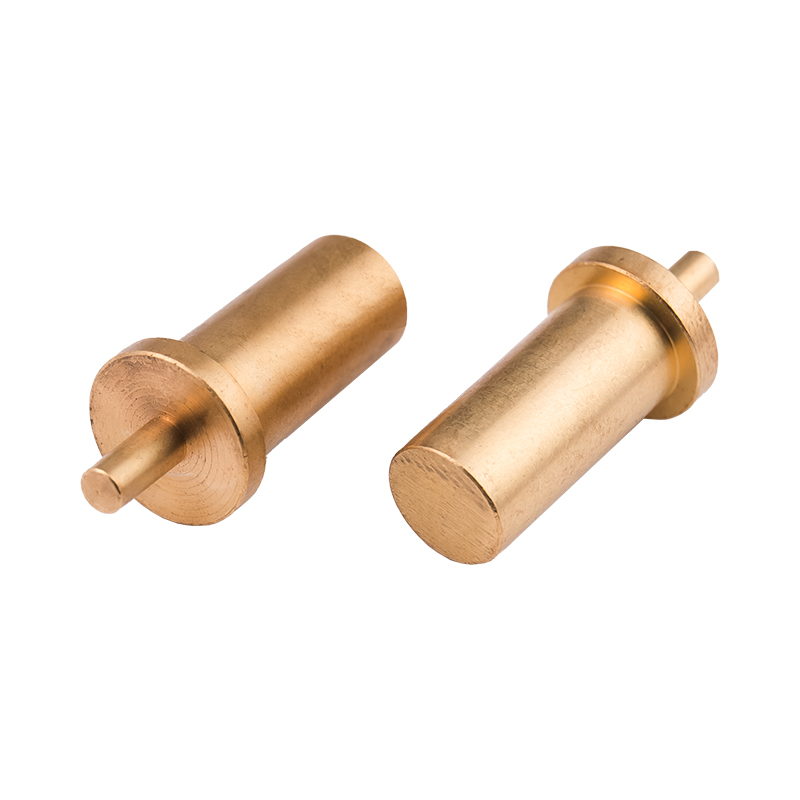
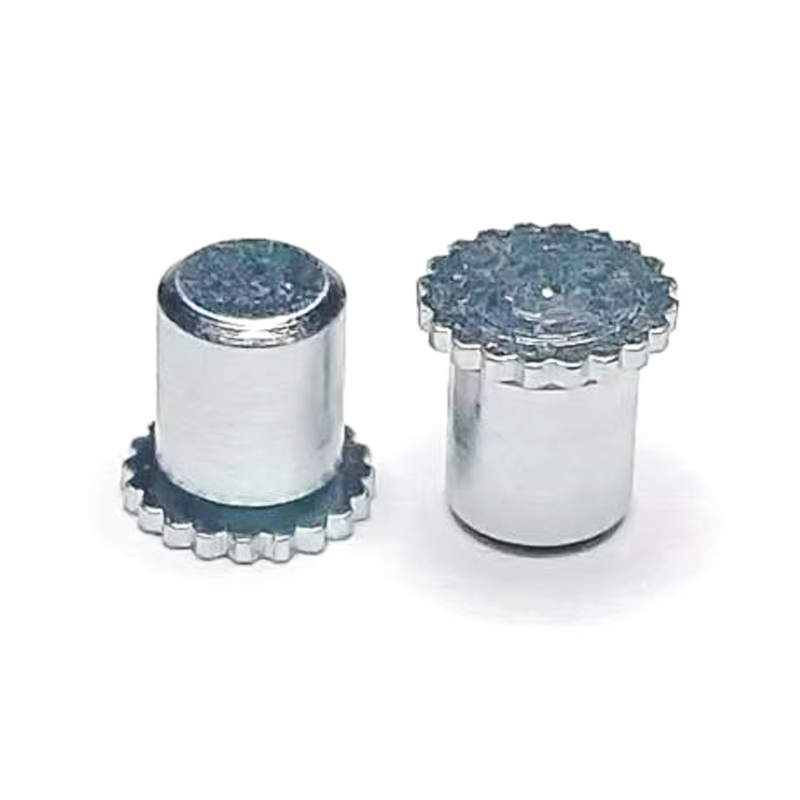
Carbon Steel Bolt Supplier Guide: What Buyers Should Look For Selecting the right supplier for carbon steel bolts affects product performance, safety, and long-term cost. This guide breaks down the p...
READ MOREThe company has obtained two quality system management certificates of ISO9001:2015 and IATF16949:2016.
At present, the company has been for Japan, Sweden, the United States, Singapore, Malaysia, Hong Kong and the Pearl River Delta and many other customers to provide services, now the main customers are: Japan Sharp (SHARP), Japan SMC, Japan Panasonic (Panasonic), the Swedish automobile VOVOL, etc., all the fixed assets investment of more than 30 million dollars, welcome friends from all walks of life to the factory to visit, study, consulting and come! We welcome friends from all walks of life to visit our factory, investigate, consult and come to us for sample processing.
We are looking forward to establishing a good business partnership with you with mutual trust and reciprocity!
-
-
Introduction: The Foundation of Mechanical Systems In the intricate world of modern manufacturing and engineering, machined parts form the fundamental building blocks of virtually every mechanical sys...
READ MORE -
Why Structural Integrity Matters In construction, machinery, and other industrial applications, structural integrity is crucial for safety, performance, and longevity. One of the key elements in ensur...
READ MORE -
Introduction to Stainless Steel Fasteners Stainless steel fasteners are widely used in construction, machinery, and industrial applications due to their corrosion resistance and durability. Among them...
READ MORE
What are the typical applications where non-standard cylindrical pins are preferred over standard ones?
In industries where off-the-shelf solutions are not suitable due to unique design specifications or performance demands, non-standard cylindrical pins offer tailored solutions. Custom machinery and equipment often require specialized pin sizes, shapes, or materials to ensure optimal functionality and reliability.
Applications that demand tight tolerances and precise fits benefit from non-standard cylindrical pins. These pins can be manufactured to exact specifications to achieve the desired level of precision, ensuring proper alignment and assembly of components in precision instruments, measuring devices, and optical equipment.
In environments where standard pins may corrode, degrade, or fail prematurely due to exposure to chemicals, extreme temperatures, or high levels of moisture, non-standard cylindrical pins made from corrosion-resistant materials like stainless steel or exotic alloys are preferred. Examples include marine equipment, chemical processing plants, and outdoor infrastructure.
Aerospace applications require components that meet stringent performance, reliability, and safety standards. Non-standard cylindrical pins are used in critical aerospace components such as control systems, landing gear, and engine assemblies, where precise fitment and resistance to high loads and vibrations are essential.
Non-standard cylindrical pins find applications in automotive manufacturing processes for components like engine parts, transmission systems, and suspension components. These pins may need to withstand high temperatures, heavy loads, and repetitive motion, making customization necessary to meet the specific requirements of each application.
Non-standard cylindrical pins are utilized in the manufacturing of medical devices where precision, biocompatibility, and reliability are paramount. These pins may be customized to meet the unique size and material requirements of medical instruments, implants, and diagnostic equipment.
What materials are commonly used for non-standard cylindrical pins, and what are their respective advantages and limitations?
Steel:
Advantages: Steel is widely available, strong, and durable, making it suitable for a wide range of applications. It offers good tensile and shear strength, as well as resistance to wear and deformation.
Limitations: Depending on the specific alloy and heat treatment, steel pins may be susceptible to corrosion in certain environments. Additionally, steel pins are relatively heavy compared to other materials, which may be a concern in weight-sensitive applications.
Stainless Steel:
Advantages: Stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance, making it ideal for applications where exposure to moisture, chemicals, or harsh environments is a concern. It maintains its strength and appearance over time and is available in various grades to suit different requirements.
Limitations: Stainless steel pins tend to be more expensive than carbon steel pins. While they resist corrosion well, certain aggressive environments can still cause corrosion over time.
Copper:
Advantages: Copper pins offer excellent electrical conductivity and thermal conductivity, making them suitable for applications where electrical or thermal transfer is important. Copper also has antimicrobial properties, which can be advantageous in certain medical or food processing applications.
Limitations: Copper is relatively soft compared to steel, which may limit its use in high-load or high-wear applications. Additionally, copper is prone to oxidation, which can affect its performance over time if not properly protected.
Aluminum:
Advantages: Aluminum pins are lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and offer good thermal conductivity. They are commonly used in aerospace and automotive applications where weight savings are critical.
Limitations: Aluminum is softer and less strong than steel, which may limit its use in high-load or high-wear applications. Additionally, aluminum can react with certain substances, leading to corrosion or galvanic corrosion in the presence of dissimilar metals.



 русский
русский Español
Español